
| Repair Procedures / HSC - Mylar Flexble Cable Technology / 1 of 2 |
HSC - Mylar Flexble Cable TechnologyThere
are two types of flexible cable used in telecommunications devices.
The most prevalent use is for connecting a LCD (liquid crystal display)
to a PCB (printed circuit board). Mylar technology can be recognized by the presence of solder joints, an amber dark green color and the presence of a TAB chip bonded to the cable. HSC (heat sealed connector) can be recognized by the absence of solder, sot pliable cable and black, green, yellow coloring. All Mylar technology can be repaired, reworked and replaced with a soldering iron, wire solder, solder paste or a bonding unit. HSC technology is divided into three groups each having different criteria for repair and can only be replaced with a process controlled bonding unit. For factory bonded results HSC material requires the application of controlled pressure and specific temperature for an exact time. HSC Technology HSC (heat sealed connectors) are not a soldered material, rather a flexible substrate with conductive traces attached. The joint created by bonding (electrically and mechanically attaching) the connecting end of HSC type flex cable is the HSC (HEAT SEALED CONNECTOR). The conducting traces - wires, so to speak - are filled with conductive material (fig 2)
Conductive epoxy and polymer technology, information and specifications are not readily available to the community of technicians and engineers working in the PCB environment. It is not necessary to understand the nuances of this technology to successfully deal with it in the repair of products using it, an understanding is sufficient to successful repair. To that end, it is more effective to use analogous examples to explain how to deal with equipment using the technology.
A good analogy, is to think of the flex (ribbon) connector as a flat wire harness with each wire replaced by a bead if conductive epoxy. Visualizing this bead of conductive epoxy as being much the same as a bead of caulking compound filled with metal particles will help in seeing the reasons for various time, pressure and temperature profiles which are required for different types of HSC material (fig 3)
Understanding the properties of the various HSC materials will allow an intelligent approach to repair of various products, as well as an appreciation of the restraints of their use and removal and replacement limitations.
|

 This technology was developed to provide a quick
and easy - yet reliable - interconnect method for connecting LCD
(liquid crystal displays) to printed circuit boards. Telecommunications
devices such as pagers, cell phones, two way radios, fax machines
and business telephones use this technology extensively. It is not
necessary to understand the precise mechanics of this technology
to replace or repair devices which have used HSC material; however,
a technician will be more comfortable knowing why a repair or replacement
is successful instead of only knowing how to do the replacement.
This technology was developed to provide a quick
and easy - yet reliable - interconnect method for connecting LCD
(liquid crystal displays) to printed circuit boards. Telecommunications
devices such as pagers, cell phones, two way radios, fax machines
and business telephones use this technology extensively. It is not
necessary to understand the precise mechanics of this technology
to replace or repair devices which have used HSC material; however,
a technician will be more comfortable knowing why a repair or replacement
is successful instead of only knowing how to do the replacement.
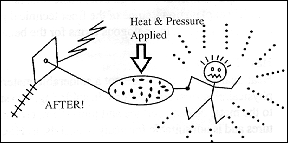
 The object of the temperature, time and pressure
profile is to get the conductive material to become plastic and
make a mechanical, as well as an electrical connection to the circuit
pad area. Different types of material require different profiles.
The object of the temperature, time and pressure
profile is to get the conductive material to become plastic and
make a mechanical, as well as an electrical connection to the circuit
pad area. Different types of material require different profiles.
 Some HSC material has different metal particles
and different amounts and sizes of metal particles. Some require
higher temperatures than others to change from the solid to the
plastic state, The pressure requirement is easily understood if
it is thought of as having to squeeze the particles together to
get them to contact each other so they will be electrically conductive
(fig 4)
Some HSC material has different metal particles
and different amounts and sizes of metal particles. Some require
higher temperatures than others to change from the solid to the
plastic state, The pressure requirement is easily understood if
it is thought of as having to squeeze the particles together to
get them to contact each other so they will be electrically conductive
(fig 4)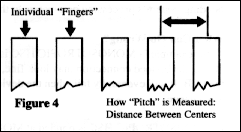 Presently, in telecommunications, there are three
main types of HSC materials in use. Each type has its own mechanical
and electrical characteristics which are unique and give a range
of price - performance features which can be applied to various
products depending on cost vs. performance considerations. The electrical
and mechanical differences as well as pitches - the spacing and
size of the trace (fig 5) - are different as well.
Presently, in telecommunications, there are three
main types of HSC materials in use. Each type has its own mechanical
and electrical characteristics which are unique and give a range
of price - performance features which can be applied to various
products depending on cost vs. performance considerations. The electrical
and mechanical differences as well as pitches - the spacing and
size of the trace (fig 5) - are different as well.
